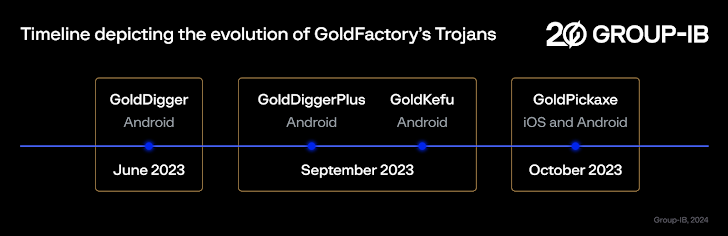
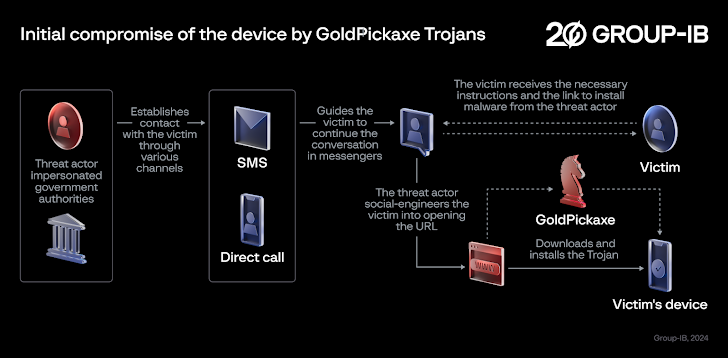
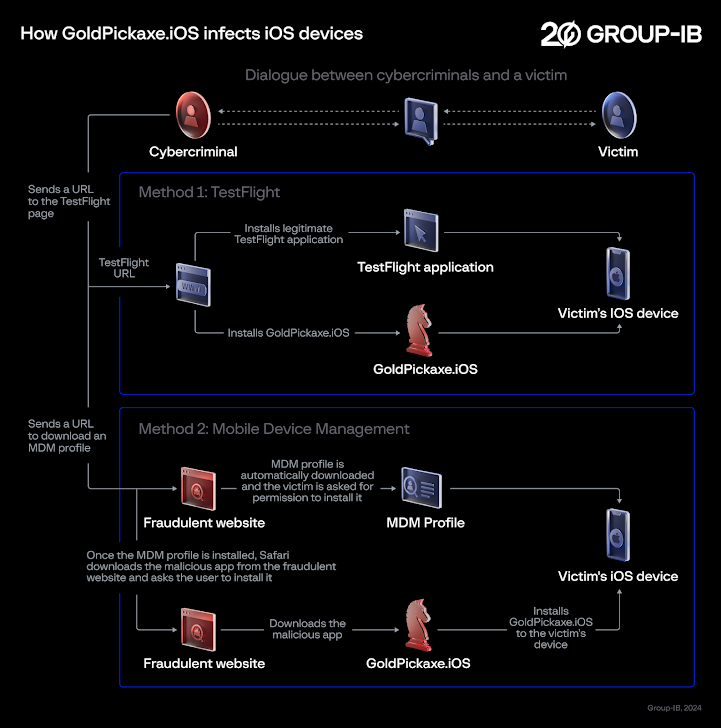
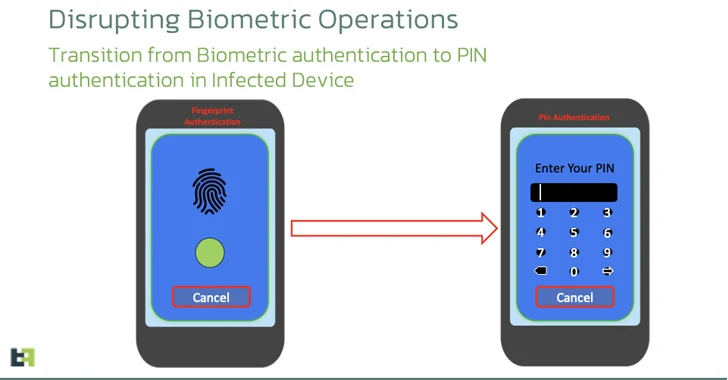
The Android banking trojan known as Vultur has resurfaced with a suite of new features and improved anti-analysis and detection evasion techniques, enabling its operators to remotely interact with a mobile device and harvest sensitive data.
“Vultur has also started masquerading more of its malicious activity by encrypting its C2 communication, using multiple encrypted payloads that are decrypted on the fly, and using the guise of legitimate applications to carry out its malicious actions,” NCC Group researcher Joshua Kamp said in a report published last week.
Vultur was first disclosed in early 2021, with the malware capable of leveraging Android’s accessibility services APIs to execute its malicious actions.
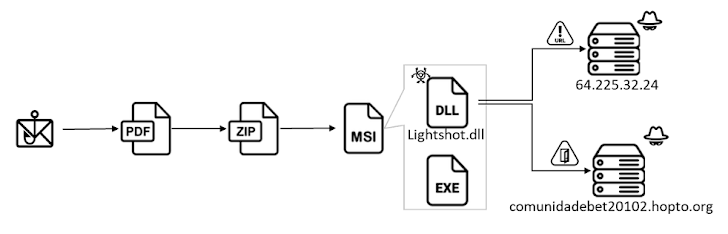
The malware has been observed to be distributed via trojanized dropper apps on the Google Play Store, masquerading as authenticator and productivity apps to trick unwitting users into installing them. These dropper apps are offered as part of a dropper-as-a-service (DaaS) operation called Brunhilda.
Other attack chains, as observed by NCC Group, involve the droppers being spread using a combination of SMS messages and phone calls – a technique called telephone-oriented attack delivery (TOAD) – to ultimately serve an updated version of the malware.
“The first SMS message guides the victim to a phone call,” Kamp said. When the victim calls the number, the fraudster provides the victim with a second SMS that includes the link to the dropper: a modified version of the [legitimate] McAfee Security app.”
The initial SMS message aims to induce a false sense of urgency by instructing the recipients to call a number to authorize a non-existent transaction that involves a large sum of money.
Upon installation, the malicious dropper executes three related payloads (two APKs and one DEX file) that register the bot with the C2 server, obtain accessibility services permissions for remote access via AlphaVNC and ngrok, and run commands fetched from the C2 server.
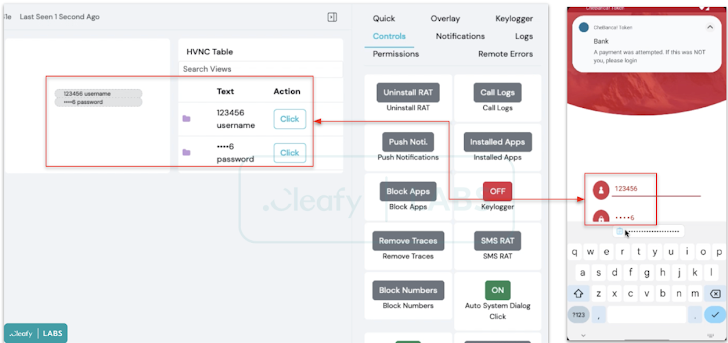
One of the prominent additions to Vultur is the ability to remotely interact with the infected device, including carrying out clicks, scrolls, and swipes, through Android’s accessibility services, as well as download, upload, delete, install, and find files.
In addition, the malware is equipped to prevent the victims from interacting with a predefined list of apps, display custom notifications in the status bar, and even disable Keyguard to bypass lock screen security measures.
“Vultur’s recent developments have shown a shift in focus towards maximizing remote control over infected devices,” Kamp said.
“With the capability to issue commands for scrolling, swipe gestures, clicks, volume control, blocking apps from running, and even incorporating file manager functionality, it is clear that the primary objective is to gain total control over compromised devices.”
The development comes as Team Cymru revealed the Octo (aka Coper) Android banking trojan’s transition to a malware-as-a-service operation, offering its services to other threat actors for conducting information theft.
“The malware offers a variety of advanced features, including keylogging, interception of SMS messages and push notifications, and control over the device’s screen,” the company said.
“It employs various injects to steal sensitive information, such as passwords and login credentials, by displaying fake screens or overlays. Additionally, it utilizes VNC (Virtual Network Computing) for remote access to devices, enhancing its surveillance capabilities.”
Octo campaigns are estimated to have compromised 45,000 devices, primarily spanning Portugal, Spain, Turkey, and the U.S. Some of the other victims are located in France, the Netherlands, Canada, India, and Japan.
The findings also follow the emergence of a new campaign targeting Android users in India that distributes malicious APK packages posing as online booking, billing, and courier services via a malware-as-a-service (MaaS) offering.
The malware “targets theft of banking information, SMS messages, and other confidential information from victims’ devices,” Broadcom-owned Symantec said in a bulletin.